Sales of Fuel Cell cars – a competitor green technology to electric vehicles, powered by energy made from mixing hydrogen and oxygen over a platinum catalyst – will meantime grow to perhaps 1 million units worldwide, Mital said.
That would prove enough to make a notable impact on auto-sector platinum demand, he said.
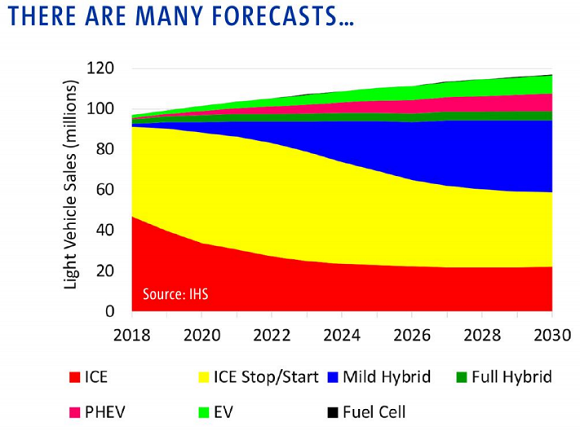
Noting there are “many different forecasts” analysts should consider, Mital said that on his assumptions global PGM usage by the auto sector “is expected to stay stable or decrease [only] marginally by 2030…with diesel sales [needing platinum catalysts] in the heavy-duty industry expected to stay steady with no change or [even a] slight increase in PGM usage as tougher regulations come into play.”
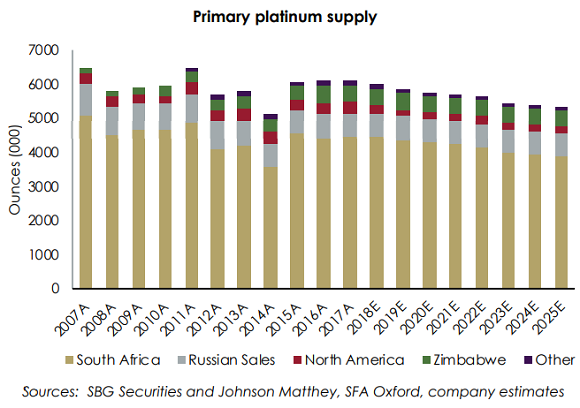
On the supply side meantime, 71% of global platinum-output comes from miners in South Africa, says a note from specialist consultants Metals Focus. So “with 90% of their costs in local currency terms, it is important to view prices in Rand terms,” and with the currency falling hard in 2018 “the Rand-denominated PGM basket price [for platinum, palladium, rhodium and gold] is up 11% for the year.”
That’s now “providing some relief to South African platinum producers,” Metals Focus says. More globally, and on an all-in sustaining costs basis for the first half of 2018, “24% of the industry is loss making, a marked improvement from 57% in H1 ’17.”
South Africa’s output of platinum-group metals
rose in September, new data showed last week, beating a 1.8% total drop in all mineral production and a near one-fifth decline in gold output with 7.2% year-on-year growth.
Further ahead however, “Supply driven deficits [are] on the horizon” for platinum worldwide reckons Justin Froneman, chief financial officer for the US at gold and platinum-group miner Sibanye-Stillwater (JSE: SGL),
also speaking at the LBMA event in Boston last month.
Since the global financial crisis of 2008 and the following drop in
platinum prices, “Capital investment in South Africa has been insufficient to replace current production levels.”
“Without incentive-driven price growth, new supply coming on-stream seems unlikely or delayed,” Froneman went on, forecasting that South Africa’s primary platinum production will drop to 3.9 million ounces in 2025, down more than 25% from the 5.3moz produced in the peak year of 2006.
“The Western Limb [of South Africa’s giant Bushveld mineral complex] currently represents more than 70% of South African supply. No new production is expected from the Western Limb without a real basket price escalation exceeding 20-25%.”
All told, “Platinum is likely to remain in marginal surplus for the remainder of this decade,” Froneman concluded, “before reverting to increasing deficits as primary production from South Africa contracts.”
Platinum’s No.1 industrial use – greater than chemical, electrical, petroleum, medical and all other productive uses combined – autocatalyst demandÂ
may slip 6% this year worldwide, buoyed by growing emerging-market usage but dented by the sharp fall in diesel passenger-vehicle sales seen in Europe since the emissions-test cheating scandal broke at VW and other leading manufacturers.